
Base Year Value ()
CAGR ()
Forecast Year Value ()
Historical Data Period
Largest Region
Forecast Period
Mercato degli enzimi per carta e cellulosa per tipo (amilasi, cellulasi, xilanasi, lipasi), applicazione (sbiancamento, deinking, modifica del prodotto) e per regione (Nord America, Europa, Asia Pacifico, Sud America, Medio Oriente e Africa), tendenze globali e previsioni dal 2020 al 2029
Instant access to hundreds of data points and trends
- Market estimates from 2014-2029
- Competitive analysis, industry segmentation, financial benchmarks
- Incorporates SWOT, Porter's Five Forces and risk management frameworks
- PDF report or online database with Word, Excel and PowerPoint export options
- 100% money back guarantee
Panoramica del mercato degli enzimi per carta e cellulosa
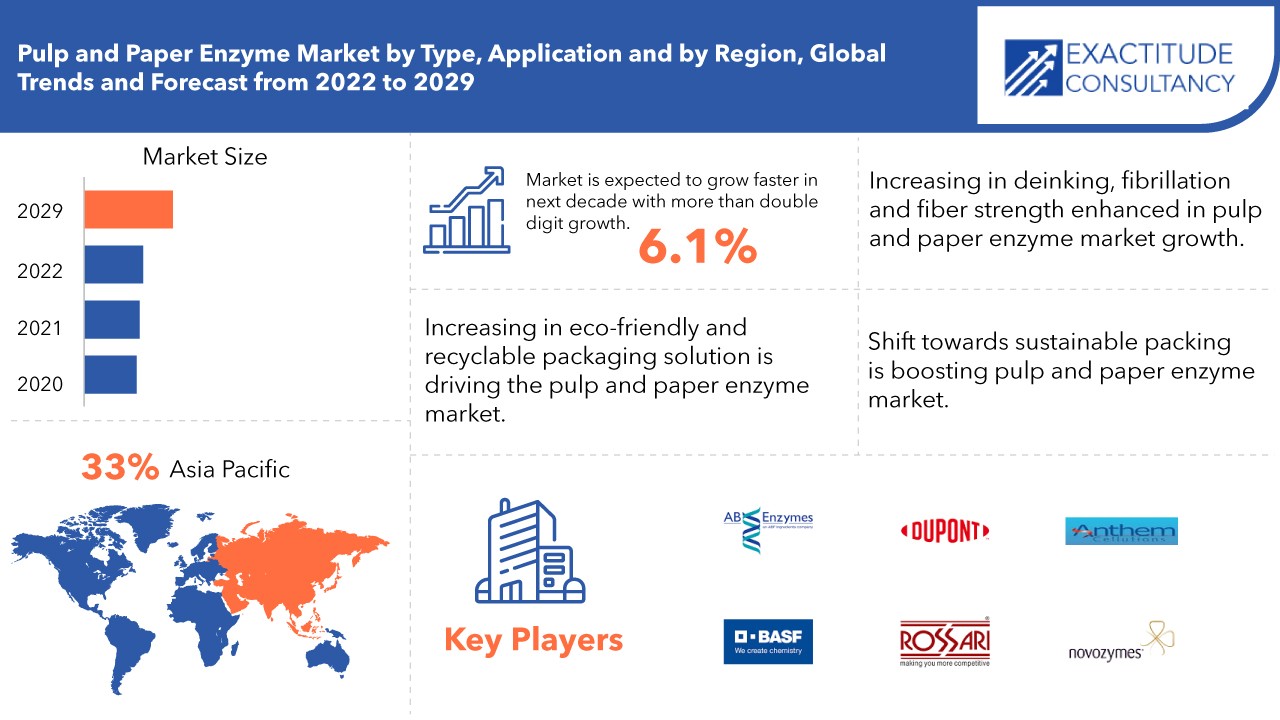
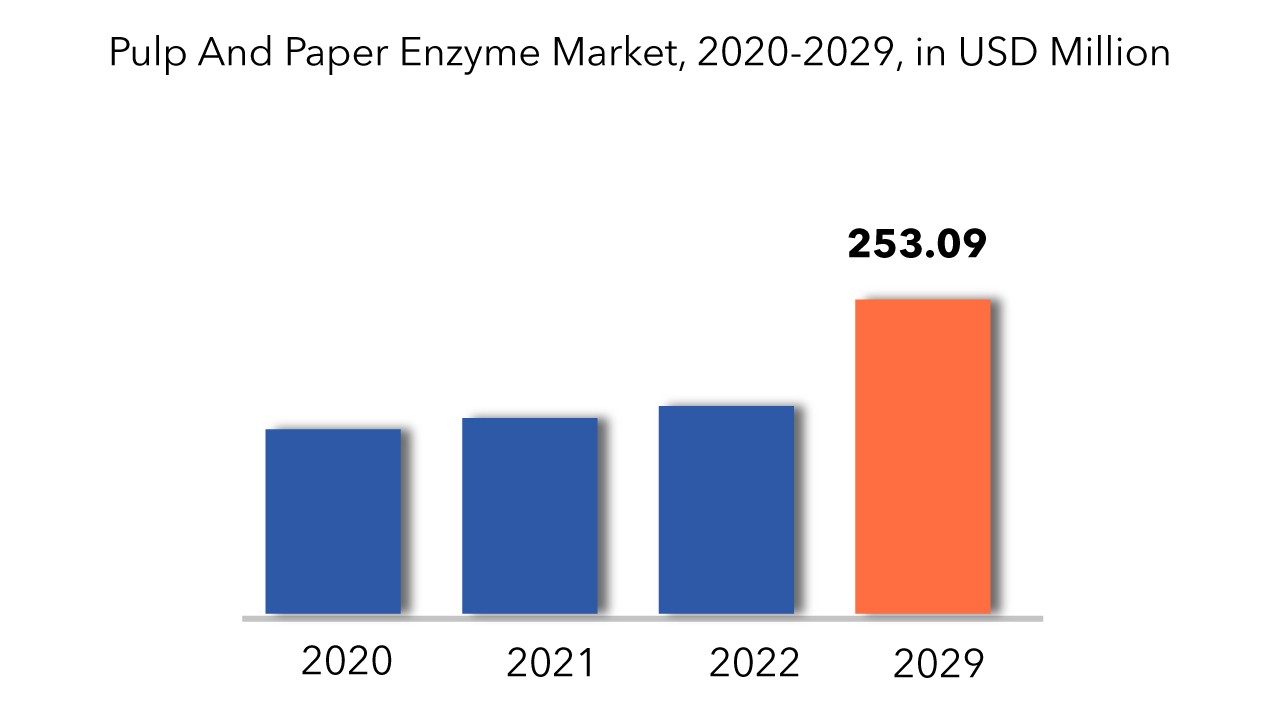
Si prevede che il mercato globale degli enzimi per carta e cellulosa raggiungerà i 253,09 milioni di USD entro il 2029, rispetto ai 148,54 milioni di USD del 2020, con un CAGR del 6,1% dal 2020 al 2029.
Gli enzimi della polpa e della carta rappresentano biocatalizzatori integrali al processo di fabbricazione della carta, che servono ad aumentare vari aspetti della lavorazione della polpa e della produzione della carta. Solitamente ricavati da microrganismi, questi enzimi possiedono caratteristiche distinte che favoriscono la scomposizione di sostanze complesse all'interno della polpa di legno, in particolare cellulosa, emicellulosa e lignina. Attraverso la catalizzazione di reazioni biochimiche, migliorano efficacemente l'efficienza dello sbiancamento della polpa, diminuiscono l'utilizzo di sostanze chimiche, rafforzano la resa della polpa e perfezionano la qualità del prodotto finale in carta. Le principali varietà di enzimi impiegate nel settore della polpa e della carta comprendono cellulasi, emicellulasi, ligninasi e perossidasi. Nel complesso, l'utilizzo di enzimi della polpa e della carta promuove pratiche di produzione della carta più sostenibili ed economicamente sostenibili.
[caption id="allegato_9215" align="aligncenter" width="870"]
Negli ultimi tempi, l' industria degli imballaggi ha registrato un aumento significativo della domanda di alternative sostenibili. Le crescenti preoccupazioni relative ai rifiuti di plastica monouso e le mutevoli preferenze dei consumatori sono fattori chiave che spingono l'adozione di imballaggi di carta , stimolando così la crescita nel dominio degli enzimi di cellulosa e carta . Inoltre, le aziende di beni di largo consumo (FMCG) sono sempre più inclini a integrare componenti ambientali, sociali e di governance (ESG) nelle loro strategie di imballaggio per affrontare diverse preoccupazioni ambientali.
Tuttavia, la fiorente tendenza verso la digitalizzazione e la comunicazione senza carta ha impedito l'espansione del settore. Molte aziende optano per la documentazione digitale e sostituti senza carta, come e-mail, sistemi di gestione dei documenti e dispositivi mobili, rispetto ai tradizionali supporti cartacei. Inoltre, la diffusa familiarità con la natura istantanea della comunicazione digitale ha portato a un calo della domanda di documenti cartacei tra la maggior parte degli individui.
[caption id="allegato_9218" align="alignnone" width="680"]
Pulp and Paper Enzyme Market Segment Analysis
The pulp and paper enzyme market is divided into three categories based on type: amylase, cellulase, xylanase, lipase. Cellulase segment is dominating the paper and pulp market. In the pulp and paper business, cellulase is used for deinking, fiber modification, and drainage enhancement. Cellulase aids in the loosening of ink from paper fibers, resulting in a faster ink removal rate. Improvements in machine run ability, improved dewatering rates, and reduced the possibility of undesired deposits are all key factors in moving the preference towards the product, resulting in increased mill productivity. Amylase is expected to grow faster in coming years. Enzyme is going to dominate the pulp and paper enzyme Surface coating, deinking, cleaning, and drainage enhancement are all possible with amylase. The product is used to modify starch, resulting in high molecular weight, low viscosity starch. Furthermore, the coating improves the sheet's smoothness, strength, and writing quality.
The market is divided into bleach boosting, deinking, product modification based on application. Bleaching is the process of removing lignin from chemical pulps, which is required for aesthetic reasons as well as improved paper qualities. Currently, considerable volumes of chlorine and chlorine compounds are used in the bleaching of Kraft pulp. Chlorinated organic compounds are byproducts of the usage of these chemicals, some of which are poisonous, mutagenic, persistent, and bio accumulative, causing a variety of biological system disruptions. Enzymes make it easy and affordable to reduce the usage of chlorine, chlorine compounds, and other bleaching agents. Enzymes also provide a straightforward method for achieving a higher brightness ceiling. Two enzyme-based techniques have been tested so far. Hemicellulase enzymes are used in one, while lignin lytic enzymes are used in the other.
Enzymatic deinking is a novel method for converting secondary fibers into high-quality products. It has been shown to be a successful and cost-effective way of deinking waste paper on a laboratory and industrial scale. Enzymatic deinking is recognized to provide a secondary benefit of improved drainage. When compared to chemically deink recycled pulps, enzymatically deinked pulps have superior physical qualities, higher brightness, and reduced residual ink. More importantly, the enzymatic technique could efficiently control the size distribution and form of ink to maximize the efficiency of the size-based flotation process. This can be done by changing the enzyme composition, charge, and residence time, as well as other additives and pH in the system, to successfully dislodge the generally massive, flat, and stiff ink particles into the system.
Pulp and Paper Enzyme Market Players
The major players operating in the global pulp and paper enzyme industry include Novozymes, Dupont, AB Enzymes, BASF SE, Biotech, Anthem Cellutions, Rossari Biotech, MetGen, Nature Bioscience, Krishna Speciality Chemicals, KPS Bio, Enzyme Solutions. These industry players are implementing several strategies such as product launches, collaborations, mergers and acquisitions to sustain industry competition and capture higher market share.
Who Should Buy? Or Key Stakeholders
- Chemical Companies
- Pulp and paper enzyme manufacturing industries
- Product modification companies
- Others
Key Takeaways:
- The global Pulp and Paper Enzyme Market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 6.1%
- Based on Type, Cellulase segment is dominating the paper and pulp market.
- Based on application, bleach boosting is dominating the paper and pulp market.
- Asia Pacific is expected to hold the largest share of the global pulp and paper enzyme market.
- The pulp and paper enzyme market is experiencing steady growth driven by increasing demand for eco-friendly and efficient production processes.
Pulp and Paper Enzyme Market Regional Analysis
Geographically, the pulp and paper enzyme market is segmented into North America, South America, Europe, APAC and MEA.
- North America: includes the US, Canada, Mexico
- Europe: includes UK, Germany, France, Italy, Spain, Russia, and Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific: includes China, Japan, South Korea, India, Australia, ASEAN and Rest of APAC
- South America: includes Brazil, Argentina and Rest of South America
- Middle East & Africa: includes Turkey, UAE, Saudi Arabia, South Africa, and Rest of MEA
Asia Pacific is expected to hold the largest share of the global pulp and paper enzyme market. The pulp & paper enzymes market is expected to grow due to a favorable increase in paper demand coupled with an expansion in end-use industries. For example, India's paper demand was approximately 15.5 million tons in 2016 and is expected to grow faster in coming years. Rapid growth in the packaging business, aided by favorable environmental regulations, is moving the industry forward. Because of the changing regulatory environment, industries such as food and beverage, cosmetics, and pharmaceuticals are increasingly using paper-based packaging. North America contributes a considerable share of pulp and paper enzyme. Technological developments, bolstered by significant product development spending, are among the primary factors fueling regional demand. The need for pulp and paper via packaging has been fueled by the growth of the processed food industry as a result of busier lifestyles. Furthermore, the easy availability of enzymes, along with a huge manufacturing capacity, is assisting in the expansion of the firm in North America.
[caption id="attachment_9219" align="alignnone" width="680"]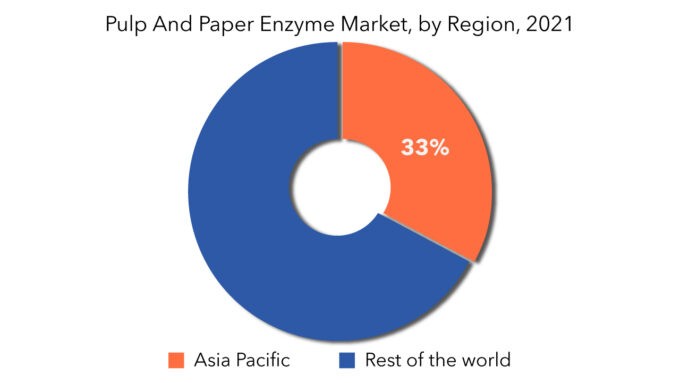
Key Market Segments: Pulp and Paper Enzyme Market
Pulp and Paper Enzyme Market by Type, 2020-2029, (USD Million) (Kilotons)- Amylase
- Cellulase
- Xylanase
- Lipase
- Bleach Boosting
- Deinking
- Product Modification
- North America
- Europe
- Asia Pacific
- South America
- Middle East and Africa
Key Question Answered
- What is the current scenario of the global pulp and paper enzyme market?
- What are the emerging technologies for the development of pulp and paper enzyme devices?
- What are the historical size and the present size of the market segments and their future potential?
- What are the major catalysts for the market and their impact during the short, medium, and long terms?
- What are the evolving opportunities for the players in the market?
- Which are the key regions from the investment perspective?
- What are the key strategies being adopted by the major players to up their market shares?
- Introduzione
- Definizione di mercato
- Segmentazione del mercato
- Research Timelines
- Assumptions and Limitations
- Research Methodology
- Data Mining
- Secondary Research
- Primary Research
- Subject-Matter Experts’ Advice
- Quality Checks
- Final Review
- Data Triangulation
- Bottom-Up Approach
- Top-Down Approach
- Research Flow
- Data Sources
- Data Mining
- Executive Summary
- Market Overview
- Global Pulp and Paper Enzyme Market Outlook
- Market Drivers
- Market Restraints
- Market Opportunities
- Impact of Covid-19 On Global Pulp and Paper Enzyme Market
- Global Pulp and Paper Enzyme Market Outlook
- Global Pulp and Paper Enzyme Market by Type, (USD Million) (Kilotons)
- Amylase
- Cellulase
- Xylanase
- Lipase
- Global Pulp and Paper Enzyme Market by Application, (USD Million) (Kilotons)
- Bleach Boosting
- Deinking
- Product Modification
- Global Pulp and Paper Enzyme Market by Region, (USD Million) (Kilotons)
- Introduction
- Asia-Pacific
- China
- India
- Japan
- South Korea
- Australia
- South-East Asia
- Rest of Asia-Pacific
- North America
- United States
- Canada
- Mexico
- Europe
- Germany
- United Kingdom
- France
- Italy
- Spain
- Russia
- Rest of Europe
- South America
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Colombia
- Rest of South America
- Middle East and Africa
- UAE
- Saudi Arabia
- South Africa
- Rest of Middle East and Africa
- Company Profiles* (Business Overview, Company Snapshot, Products Offered, Recent Developments)
- Novozymes
- Dupont
- AB Enzymes
- BASF SE
- Biotech
- Anthem Cellutions
- Rossari Biotech
- MetGen
- Nature Bioscience
- KPS Bio
- Others *The Company List Is Indicative
LIST OF TABLES
TABLE 1 GLOBAL PULP AND PAPER ENZYME MARKET BY Type (USD MILLIONS), 2020-2029
TABLE 2 GLOBAL PULP AND PAPER ENZYME MARKET BY Type (KILOTONS), 2020-2029
TABLE 3 GLOBAL PULP AND PAPER ENZYME MARKET BY APPLICATION (USD MILLIONS), 2020-2029
TABLE 4 GLOBAL PULP AND PAPER ENZYME MARKET BY APPLICATION (KILOTONS), 2020-2029
TABLE 5 GLOBAL PULP AND PAPER ENZYME MARKET BY REGION (USD MILLIONS), 2020-2029
TABLE 6 GLOBAL PULP AND PAPER ENZYME MARKET BY REGION (KILOTONS), 2020-2029
TABLE 7 NORTH AMERICA PULP AND PAPER ENZYME MARKET BY COUNTRY (USD MILLIONS), 2020-2029
TABLE 8 NORTH AMERICA PULP AND PAPER ENZYME MARKET BY COUNTRY (KILOTONS), 2020-2029
TABLE 9 US PULP AND PAPER ENZYME MARKET BY Type (USD MILLIONS), 2020-2029
TABLE 10 US PULP AND PAPER ENZYME MARKET BY Type (KILOTONS), 2020-2029
TABLE 11 US PULP AND PAPER ENZYME MARKET BY APPLICATION (USD MILLIONS), 2020-2029
TABLE 12 US PULP AND PAPER ENZYME MARKET BY APPLICATION (KILOTONS), 2020-2029
TABLE 13 Canada PULP AND PAPER ENZYME MARKET BY Type (USD MILLIONS), 2020-2029
TABLE 14 Canada PULP AND PAPER ENZYME MARKET BY Type (KILOTONS), 2020-2029
TABLE 15 Canada PULP AND PAPER ENZYME MARKET BY APPLICATION (USD MILLIONS), 2020-2029
TABLE 16 Canada PULP AND PAPER ENZYME MARKET BY APPLICATION (KILOTONS), 2020-2029
TABLE 17 MEXICO PULP AND PAPER ENZYME MARKET BY Type (USD MILLIONS), 2020-2029
TABLE 18 MEXICO PULP AND PAPER ENZYME MARKET BY Type (KILOTONS), 2020-2029
TABLE 19 MEXICO PULP AND PAPER ENZYME MARKET BY APPLICATION (USD MILLIONS), 2020-2029
TABLE 20 MEXICO PULP AND PAPER ENZYME MARKET BY APPLICATION (KILOTONS), 2020-2029
TABLE 21 SOUTH AMERICA PULP AND PAPER ENZYME MARKET BY COUNTRY (USD MILLIONS), 2020-2029
TABLE 22 SOUTH AMERICA PULP AND PAPER ENZYME MARKET BY COUNTRY (KILOTONS), 2020-2029
TABLE 23 BRAZIL PULP AND PAPER ENZYME MARKET BY Type (USD MILLIONS), 2020-2029
TABLE 24 BRAZIL PULP AND PAPER ENZYME MARKET BY Type (KILOTONS), 2020-2029
TABLE 25 BRAZIL PULP AND PAPER ENZYME MARKET BY APPLICATION (USD MILLIONS), 2020-2029
TABLE 26 BRAZIL PULP AND PAPER ENZYME MARKET BY APPLICATION (KILOTONS), 2020-2029
TABLE 27 ARGENTINA PULP AND PAPER ENZYME MARKET BY Type (USD MILLIONS), 2020-2029
TABLE 28 ARGENTINA PULP AND PAPER ENZYME MARKET BY Type (KILOTONS), 2020-2029
TABLE 29 ARGENTINA PULP AND PAPER ENZYME MARKET BY APPLICATION (USD MILLIONS), 2020-2029
TABLE 30 ARGENTINA PULP AND PAPER ENZYME MARKET BY APPLICATION (KILOTONS), 2020-2029
TABLE 31 COLOMBIA PULP AND PAPER ENZYME MARKET BY Type (USD MILLIONS), 2020-2029
TABLE 32 COLOMBIA PULP AND PAPER ENZYME MARKET BY Type (KILOTONS), 2020-2029
TABLE 33 COLOMBIA PULP AND PAPER ENZYME MARKET BY APPLICATION (USD MILLIONS), 2020-2029
TABLE 34 COLOMBIA PULP AND PAPER ENZYME MARKET BY APPLICATION (KILOTONS), 2020-2029
TABLE 35 REST OF SOUTH AMERICA PULP AND PAPER ENZYME MARKET BY Type (USD MILLIONS), 2020-2029
TABLE 36 REST OF SOUTH AMERICA PULP AND PAPER ENZYME MARKET BY Type (KILOTONS), 2020-2029
TABLE 37 REST OF SOUTH AMERICA PULP AND PAPER ENZYME MARKET BY APPLICATION (USD MILLIONS), 2020-2029
TABLE 38 REST OF SOUTH AMERICA PULP AND PAPER ENZYME MARKET BY APPLICATION (KILOTONS), 2020-2029
TABLE 39 ASIA-PACIFIC PULP AND PAPER ENZYME MARKET BY COUNTRY (USD MILLIONS), 2020-2029
TABLE 40 ASIA-PACIFIC PULP AND PAPER ENZYME MARKET BY COUNTRY (KILOTONS), 2020-2029
TABLE 41 INDIA PULP AND PAPER ENZYME MARKET BY Type (USD MILLIONS), 2020-2029
TABLE 42 INDIA PULP AND PAPER ENZYME MARKET BY Type (KILOTONS), 2020-2029
TABLE 43 INDIA PULP AND PAPER ENZYME MARKET BY APPLICATION (USD MILLIONS), 2020-2029
TABLE 44 INDIA PULP AND PAPER ENZYME MARKET BY APPLICATION (KILOTONS), 2020-2029
TABLE 45 CHINA PULP AND PAPER ENZYME MARKET BY Type (USD MILLIONS), 2020-2029
TABLE 46 CHINA PULP AND PAPER ENZYME MARKET BY Type (KILOTONS), 2020-2029
TABLE 47 CHINA PULP AND PAPER ENZYME MARKET BY APPLICATION (USD MILLIONS), 2020-2029
TABLE 48 CHINA PULP AND PAPER ENZYME MARKET BY APPLICATION (KILOTONS), 2020-2029
TABLE 49 JAPAN PULP AND PAPER ENZYME MARKET BY Type (USD MILLIONS), 2020-2029
TABLE 50 JAPAN PULP AND PAPER ENZYME MARKET BY Type (KILOTONS), 2020-2029
TABLE 51 JAPAN PULP AND PAPER ENZYME MARKET BY APPLICATION (USD MILLIONS), 2020-2029
TABLE 52 JAPAN PULP AND PAPER ENZYME MARKET BY APPLICATION (KILOTONS), 2020-2029
TABLE 53 SOUTH KOREA PULP AND PAPER ENZYME MARKET BY Type (USD MILLIONS), 2020-2029
TABLE 54 SOUTH KOREA PULP AND PAPER ENZYME MARKET BY Type (KILOTONS), 2020-2029
TABLE 55 SOUTH KOREA PULP AND PAPER ENZYME MARKET BY APPLICATION (USD MILLIONS), 2020-2029
TABLE 56 SOUTH KOREA PULP AND PAPER ENZYME MARKET BY APPLICATION (KILOTONS), 2020-2029
TABLE 57 AUSTRALIA PULP AND PAPER ENZYME MARKET BY Type (USD MILLIONS), 2020-2029
TABLE 58 AUSTRALIA PULP AND PAPER ENZYME MARKET BY Type (KILOTONS), 2020-2029
TABLE 59 AUSTRALIA PULP AND PAPER ENZYME MARKET BY APPLICATION (USD MILLIONS), 2020-2029
TABLE 60 AUSTRALIA PULP AND PAPER ENZYME MARKET BY APPLICATION (KILOTONS), 2020-2029
TABLE 61 SOUTH EAST ASIA PULP AND PAPER ENZYME MARKET BY Type (USD MILLIONS), 2020-2029
TABLE 62 SOUTH EAST ASIA PULP AND PAPER ENZYME MARKET BY Type (KILOTONS), 2020-2029
TABLE 63 SOUTH EAST ASIA PULP AND PAPER ENZYME MARKET BY APPLICATION (USD MILLIONS), 2020-2029
TABLE 64 SOUTH EAST ASIA PULP AND PAPER ENZYME MARKET BY APPLICATION (KILOTONS), 2020-2029
TABLE 65 REST OF ASIA PACIFIC PULP AND PAPER ENZYME MARKET BY Type (USD MILLIONS), 2020-2029
TABLE 66 REST OF ASIA PACIFIC PULP AND PAPER ENZYME MARKET BY Type (KILOTONS), 2020-2029
TABLE 67 REST OF ASIA PACIFIC PULP AND PAPER ENZYME MARKET BY APPLICATION (USD MILLIONS), 2020-2029
TABLE 68 REST OF ASIA PACIFIC PULP AND PAPER ENZYME MARKET BY APPLICATION (KILOTONS), 2020-2029
TABLE 69 EUROPE PULP AND PAPER ENZYME MARKET BY COUNTRY (USD MILLIONS), 2020-2029
TABLE 70 EUROPE PULP AND PAPER ENZYME MARKET BY COUNTRY (KILOTONS), 2020-2029
TABLE 71 GERMANY PULP AND PAPER ENZYME MARKET BY Type (USD MILLIONS), 2020-2029
TABLE 72 GERMANY PULP AND PAPER ENZYME MARKET BY Type (KILOTONS), 2020-2029
TABLE 73 GERMANY PULP AND PAPER ENZYME MARKET BY APPLICATION (USD MILLIONS), 2020-2029
TABLE 74 GERMANY PULP AND PAPER ENZYME MARKET BY APPLICATION (KILOTONS), 2020-2029
TABLE 75 UK PULP AND PAPER ENZYME MARKET BY Type (USD MILLIONS), 2020-2029
TABLE 76 UK PULP AND PAPER ENZYME MARKET BY Type (KILOTONS), 2020-2029
TABLE 77 UK PULP AND PAPER ENZYME MARKET BY APPLICATION (USD MILLIONS), 2020-2029
TABLE 78 UK PULP AND PAPER ENZYME MARKET BY APPLICATION (KILOTONS), 2020-2029
TABLE 79 FRANCE PULP AND PAPER ENZYME MARKET BY Type (USD MILLIONS), 2020-2029
TABLE 80 FRANCE PULP AND PAPER ENZYME MARKET BY Type (KILOTONS), 2020-2029
TABLE 81 FRANCE PULP AND PAPER ENZYME MARKET BY APPLICATION (USD MILLIONS), 2020-2029
TABLE 82 FRANCE PULP AND PAPER ENZYME MARKET BY APPLICATION (KILOTONS), 2020-2029
TABLE 83 ITALY PULP AND PAPER ENZYME MARKET BY Type (USD MILLIONS), 2020-2029
TABLE 84 ITALY PULP AND PAPER ENZYME MARKET BY Type (KILOTONS), 2020-2029
TABLE 85 ITALY PULP AND PAPER ENZYME MARKET BY APPLICATION (USD MILLIONS), 2020-2029
TABLE 86 ITALY PULP AND PAPER ENZYME MARKET BY APPLICATION (KILOTONS), 2020-2029
TABLE 87 SPAIN PULP AND PAPER ENZYME MARKET BY Type (USD MILLIONS), 2020-2029
TABLE 88 SPAIN PULP AND PAPER ENZYME MARKET BY Type (KILOTONS), 2020-2029
TABLE 89 SPAIN PULP AND PAPER ENZYME MARKET BY APPLICATION (USD MILLIONS), 2020-2029
TABLE 90 SPAIN PULP AND PAPER ENZYME MARKET BY APPLICATION (KILOTONS), 2020-2029
TABLE 91 RUSSIA PULP AND PAPER ENZYME MARKET BY Type (USD MILLIONS), 2020-2029
TABLE 92 RUSSIA PULP AND PAPER ENZYME MARKET BY Type (KILOTONS), 2020-2029
TABLE 93 RUSSIA PULP AND PAPER ENZYME MARKET BY APPLICATION (USD MILLIONS), 2020-2029
TABLE 94 RUSSIA PULP AND PAPER ENZYME MARKET BY APPLICATION (KILOTONS), 2020-2029
TABLE 95 REST OF EUROPE PULP AND PAPER ENZYME MARKET BY Type (USD MILLIONS), 2020-2029
TABLE 96 REST OF EUROPE PULP AND PAPER ENZYME MARKET BY Type (KILOTONS), 2020-2029
TABLE 97 REST OF EUROPE PULP AND PAPER ENZYME MARKET BY APPLICATION (USD MILLIONS), 2020-2029
TABLE 98 REST OF EUROPE PULP AND PAPER ENZYME MARKET BY APPLICATION (KILOTONS), 2020-2029
TABLE 99 MIDDLE EAST AND AFRICA PULP AND PAPER ENZYME MARKET BY COUNTRY (USD MILLIONS), 2020-2029
TABLE 100 MIDDLE EAST AND AFRICA PULP AND PAPER ENZYME MARKET BY COUNTRY (KILOTONS), 2020-2029
TABLE 101 UAE PULP AND PAPER ENZYME MARKET BY Type (USD MILLIONS), 2020-2029
TABLE 102 UAE PULP AND PAPER ENZYME MARKET BY Type (KILOTONS), 2020-2029
TABLE 103 UAE PULP AND PAPER ENZYME MARKET BY APPLICATION (USD MILLIONS), 2020-2029
TABLE 104 UAE PULP AND PAPER ENZYME MARKET BY APPLICATION (KILOTONS), 2020-2029
TABLE 105 SAUDI ARABIA PULP AND PAPER ENZYME MARKET BY Type (USD MILLIONS), 2020-2029
TABLE 106 SAUDI ARABIA PULP AND PAPER ENZYME MARKET BY Type (KILOTONS), 2020-2029
TABLE 107 SAUDI ARABIA PULP AND PAPER ENZYME MARKET BY APPLICATION (USD MILLIONS), 2020-2029
TABLE 108 SAUDI ARABIA PULP AND PAPER ENZYME MARKET BY APPLICATION (KILOTONS), 2020-2029
TABLE 109 SOUTH AFRICA PULP AND PAPER ENZYME MARKET BY Type (USD MILLIONS), 2020-2029
TABLE 110 SOUTH AFRICA PULP AND PAPER ENZYME MARKET BY Type (KILOTONS), 2020-2029
TABLE 111 SOUTH AFRICA PULP AND PAPER ENZYME MARKET BY APPLICATION (USD MILLIONS), 2020-2029
TABLE 112 SOUTH AFRICA PULP AND PAPER ENZYME MARKET BY APPLICATION (KILOTONS), 2020-2029
TABLE 113 REST OF MIDDLE EAST AND AFRICA PULP AND PAPER ENZYME MARKET BY Type (USD MILLIONS), 2020-2029
TABLE 114 REST OF MIDDLE EAST AND AFRICA PULP AND PAPER ENZYME MARKET BY Type (KILOTONS), 2020-2029
TABLE 115 REST OF MIDDLE EAST AND AFRICA PULP AND PAPER ENZYME MARKET BY APPLICATION (USD MILLIONS), 2020-2029
TABLE 116 REST OF MIDDLE EAST AND AFRICA PULP AND PAPER ENZYME MARKET BY APPLICATION (KILOTONS), 2020-2029
LIST OF FIGURES
FIGURE 1 MARKET DYNAMICS
FIGURE 2 MARKET SEGMENTATION
FIGURE 3 REPORT TIMELINES: YEARS CONSIDERED
FIGURE 4 DATA TRIANGULATION
FIGURE 5 BOTTOM-UP APPROACH
FIGURE 6 TOP-DOWN APPROACH
FIGURE 7 RESEARCH FLOW
FIGURE 8 GLOBAL PULP AND PAPER ENZYME MARKET BY TYPE, USD MILLION, 2020-2029
FIGURE 9 GLOBAL PULP AND PAPER ENZYME MARKET BY APPLICATION, USD MILLION, 2020-2029
FIGURE 10 GLOBAL PULP AND PAPER ENZYME MARKET BY REGION, USD MILLION, 2020-2029
FIGURE 11 PORTER’S FIVE FORCES MODEL
FIGURE 12 GLOBAL PULP AND PAPER ENZYME MARKET BY TYPE, USD MILLION, 2020-2029
FIGURE 13 GLOBAL PULP AND PAPER ENZYME MARKET BY APPLICATION, USD MILLION, 2020-2029
FIGURE 14 GLOBAL PULP AND PAPER ENZYME MARKET BY REGION, USD MILLION, 2020-2029
FIGURE 15 PULP AND PAPER ENZYME MARKET BY REGION 2020
FIGURE 16 MARKET SHARE ANALYSIS
FIGURE 17 NOVOZYMES: COMPANY SNAPSHOT
FIGURE 18 DUPONT: COMPANY SNAPSHOT
FIGURE 19 AB ENZYMES: COMPANY SNAPSHOT
FIGURE 20 BASF SE: COMPANY SNAPSHOT
FIGURE 21 BIOTECH: COMPANY SNAPSHOT
FIGURE 22 ANTHEM CELLUTIONS: COMPANY SNAPSHOT
FIGURE 23 ROSSARI BIOTECH: COMPANY SNAPSHOT
FIGURE 24 METGEN: COMPANY SNAPSHOT
FIGURE 25 NATURE BIOSCIENCE: COMPANY SNAPSHOT
FIGURE 26 KPS BIO: COMPANY SNAPSHOT
DOWNLOAD FREE SAMPLE REPORT
License Type
SPEAK WITH OUR ANALYST
Want to know more about the report or any specific requirement?
WANT TO CUSTOMIZE THE REPORT?
Our Clients Speak
We asked them to research ‘ Equipment market’ all over the world, and their whole arrangement was helpful to us. thehealthanalytics.com insightful analysis and reports contributed to our current analysis and in creating a future strategy. Besides, the te
Yosuke Mitsui
Senior Associate Construction Equipment Sales & Marketing
We asked them to research ‘Equipment market’ all over the world, and their whole arrangement was helpful to us. thehealthanalytics.com insightful analysis and reports contributed to our current analysis and in creating a future strategy. Besides, the te






