
Base Year Value ()
CAGR ()
Forecast Year Value ()
Historical Data Period
Largest Region
Forecast Period
Mercato degli scanner per risonanza magnetica per intensità di campo (sistemi MRI a campo basso-medio (da 0,5 T a 1,5 T), sistemi MRI ad alto campo (da 1,5 T a 3 T), sistemi MRI ad altissimo campo (da 3 T a 7 T), sistemi MRI ad altissimo campo (da 7 T e oltre)), applicazione (neurologia, muscoloscheletrico, oncologia, cardiovascolare, altre applicazioni), utente finale (ospedali, centri di diagnostica per immagini, altri utenti finali) e regione, tendenze globali e previsioni dal 2024 al 2030
Instant access to hundreds of data points and trends
- Market estimates from 2014-2029
- Competitive analysis, industry segmentation, financial benchmarks
- Incorporates SWOT, Porter's Five Forces and risk management frameworks
- PDF report or online database with Word, Excel and PowerPoint export options
- 100% money back guarantee
Panoramica del mercato
Si prevede che il mercato globale degli scanner per risonanza magnetica crescerà da 7,72 miliardi di USD nel 2023 a 11,96 miliardi di USD entro il 2030, con un CAGR del 6,45% nel periodo di previsione.
Gli scanner per risonanza magnetica (MRI) sono dispositivi medici sofisticati che utilizzano i principi della risonanza magnetica nucleare per produrre immagini dettagliate e ad alta risoluzione delle strutture interne del corpo umano. Quando un paziente viene posizionato all'interno della macchina MRI, che consiste in un forte campo magnetico e bobine a radiofrequenza, gli atomi di idrogeno si allineano con il campo magnetico. Successivamente, viene applicato un impulso a radiofrequenza, interrompendo temporaneamente questo allineamento. Quando gli atomi di idrogeno tornano al loro allineamento originale, emettono segnali che vengono rilevati dalla macchina MRI. Analizzando i segnali emessi, un computer genera immagini trasversali delle strutture interne del corpo, come organi, tessuti e ossa.
L'intensità del campo magnetico, misurata in Tesla, gioca un ruolo cruciale nella risoluzione e nella qualità delle immagini. Intensità di campo magnetico più elevate generalmente danno come risultato immagini più nitide e dettagliate. Gli scanner MRI possono produrre immagini su vari piani, consentendo una visualizzazione completa delle strutture anatomiche. Inoltre, tecniche avanzate come l'aumento del contrasto, la risonanza magnetica funzionale e l'imaging pesato in diffusione forniscono ulteriori approfondimenti sulle caratteristiche e le funzioni dei tessuti.
La natura non invasiva della RM, senza l'uso di radiazioni ionizzanti, la rende una modalità di imaging preferita per la diagnosi di un'ampia gamma di condizioni mediche, tra cui disturbi neurologici, problemi muscoloscheletrici e anomalie dei tessuti molli. La versatilità degli scanner RM nel catturare strutture interne dettagliate con il minimo disagio per il paziente li ha resi uno strumento indispensabile nella medicina moderna sia per scopi diagnostici che di ricerca.
[caption id="allegato_38420" align="aligncenter" width="839"]

Technological developments are crucial; they improve the functionality, efficiency, and image quality of MRI scanners. MRI is becoming a more effective and diverse diagnostic tool due to ongoing research and development efforts that have produced better imaging sequences, higher field strengths, and sophisticated software algorithms. The global aging population and the rising incidence of chronic illnesses have also raised the need for precise, non-invasive diagnostic techniques, which has expanded demand for MRI scanners.
In addition, MRI's growing range of uses, from neurology and orthopedics to cardiology and oncology, has expanded its usefulness in a number of medical disciplines. These uses include functional and molecular imaging. The growing need for these scanners in healthcare facilities is a result of the emphasis on early and accurate diagnosis as well as growing knowledge of the advantages of MRI. In addition, government programs to improve healthcare infrastructure and favorable reimbursement rules have made it easier for MRI technology to be adopted in both developed and developing nations.
Precision diagnosis and treatment planning for a variety of medical diseases are made possible by the comprehensive and non-invasive internal structural imaging that MRI scanners provide. Where they differ from other imaging modalities like computed tomography (CT) or X-rays is that they can provide higher-resolution images of soft tissues, organs, and the central nervous system. As a result, MRI is especially important for the identification and diagnosis of a number of diseases, such as oncological abnormalities, musculoskeletal problems, neurological disorders, and cardiovascular diseases.
MRI is a safer alternative for recurrent imaging, particularly for susceptible groups like children and pregnant women, because it is non-ionizing and does not expose patients to hazardous radiation. Early detection, prompt therapies, and improved patient outcomes are all made possible by the diagnostic precision offered by MRI scanners. Furthermore, these scanners are kept at the forefront of medical imaging capabilities by the ongoing advancement of MRI technology, which is fueled by research and development initiatives.
| ATTRIBUTE | DETAILS |
| Study period | 2020-2030 |
| Base year | 2022 |
| Estimated year | 2023 |
| Forecasted year | 2023-2030 |
| Historical period | 2019-2021 |
| Unit | Value (USD Billion) Volume (Thousand Units) |
| Segmentation | By Field Strength, End-user, Application and Region |
| By Field Strength |
|
| By Application |
|
| By End User |
|
| By Region |
|
Frequently Asked Questions
• What is the market size for the magnetic resonance imaging scanners market?
The global magnetic resonance imaging scanners market is anticipated to grow from USD 7.72 Billion in 2023 to USD 11.96 Billion by 2030, at a CAGR of 6.45 % during the forecast period.
• Which region is dominating in the magnetic resonance imaging scanners market?
Asia-Pacific accounted for the largest market in the magnetic resonance imaging scanners market. Asia-Pacific accounted for 40 % market share of the global market value.
• Who are the major key players in the magnetic resonance imaging scanners market?
Siemens Healthineers, GE Healthcare, Philips Healthcare, Toshiba Medical Systems Corporation, Hitachi Medical Corporation, Bruker Corporation, Esaote SpA, Fonar Corporation, Mindray Medical International Limited, Neusoft Medical Systems Co., Ltd., Samsung Medison Co., Ltd., Shenzhen Anke High-tech Co., Ltd., Time Medical Systems Co., Ltd., AllTech Medical Systems America, Inc., Aspect Imaging Ltd., Aurigin Technology Inc., CMR Naviscan Corporation, Cubresa Inc., Mediso Ltd., MR Solutions Ltd.
• What are the key trends in the magnetic resonance imaging scanners market?
Key trends in the magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scanners market include the growing adoption of artificial intelligence (AI) for enhanced imaging interpretation, the development of more compact and portable MRI scanners for increased accessibility, and a focus on advanced applications such as functional MRI (fMRI) for neurological studies and precision medicine. Additionally, there is a continuous emphasis on improving patient comfort and experience during MRI examinations.
Magnetic Resonance Imaging Scanners Market Segmentation Analysis
The global Magnetic Resonance Imaging Scanners market is divided into three segments, field strength, application, end-user and region. By field strength the market is divided Low-to-mid-field MRI systems (0.5T to 1.5T), High-field MRI systems (1.5T to 3T), Very-high-field MRI systems (3T to 7T), Ultra-high-field MRI systems (7T and above). By application the market is classified into Neurology, Musculoskeletal, Oncology, Cardiovascular, Other Applications. By end-user the market is classified into Hospitals, Diagnostic Imaging Centers, Other End Users.
[caption id="attachment_38430" align="aligncenter" width="733"]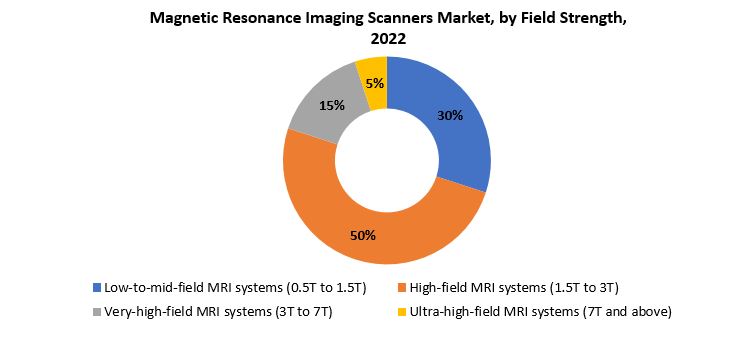
Based on field strength, high-field MRI systems (1.5T to 3T) segment dominating in the magnetic resonance imaging scanners market. High-field MRI systems offer superior image resolution and quality compared to lower field strengths, enabling clinicians to obtain detailed and clearer images of anatomical structures and pathological conditions. The 1.5T to 3T range strikes a balance between image quality and practical considerations such as cost and patient comfort, making these systems widely adopted in clinical settings.
The higher magnetic field strength enhances signal-to-noise ratios, which is crucial for improving image clarity and reducing the need for contrast agents in certain examinations. This is particularly advantageous in imaging soft tissues, neurological structures, and musculoskeletal components, where precise visualization is critical for accurate diagnosis and treatment planning. High-field MRI systems also facilitate advanced imaging techniques such as functional MRI (fMRI) and magnetic resonance angiography (MRA), expanding their applications across various medical specialties.
Furthermore, technological advancements in superconducting magnets and radiofrequency coils have contributed to the increased efficiency and performance of high-field MRI systems. The ability to acquire images faster and with better signal strength enhances the overall workflow in healthcare facilities, improving patient throughput and diagnostic accuracy. Despite their higher upfront costs, the long-term benefits of improved diagnostic capabilities and versatility make high-field MRI systems a preferred choice for many healthcare providers.
[caption id="attachment_38431" align="aligncenter" width="691"]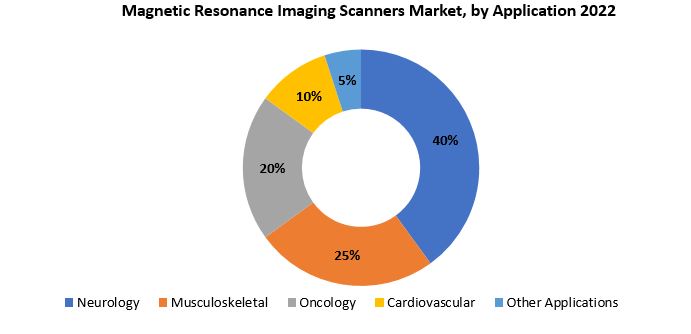
Based on application, neurology segment dominating in the magnetic resonance imaging scanners market. Neurological disorders, including brain and spinal cord conditions, demand precise and detailed imaging for accurate diagnosis and treatment planning, making MRI an indispensable tool in neurology. The high-resolution capabilities of MRI scanners allow for the visualization of intricate structures within the brain, enabling healthcare professionals to identify abnormalities such as tumors, vascular malformations, and degenerative diseases with exceptional clarity.
Neurological applications of MRI extend beyond structural imaging, encompassing functional MRI (fMRI) for mapping brain activity, diffusion-weighted imaging for assessing tissue microstructure, and magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS) for studying chemical composition. These advanced techniques contribute to a comprehensive understanding of neurological conditions, aiding in early detection and providing critical information for surgical planning or therapeutic interventions.
The non-invasive nature of MRI is particularly advantageous in neurology, as it eliminates the need for invasive procedures and minimizes patient discomfort. Additionally, the versatility of MRI allows for multi-parametric imaging, enabling clinicians to evaluate different aspects of neurological health in a single examination. The neurology segment's dominance is further fueled by the rising incidence of neurological disorders globally, driven by factors such as aging populations, increased awareness, and evolving lifestyles.
[caption id="attachment_38432" align="aligncenter" width="652"]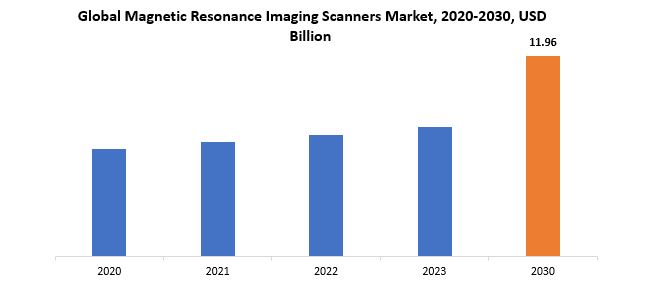
Magnetic Resonance Imaging Scanners Market Dynamics
DriverRising prevalence of chronic diseases boosts demand for magnetic resonance imaging scanners market.
Chronic diseases, which include afflictions like cancer, neurological disorders, musculoskeletal ailments, and cardiovascular diseases, are on the rise worldwide as a result of factors including sedentary lifestyles, aging populations, and eating habits. Since many chronic illnesses require constant observation, prompt and correct diagnosis is essential to efficient treatment planning and administration. In this context, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scanners are essential tools because they provide high-resolution imaging capabilities that let medical practitioners see and evaluate soft tissues, organs, and structures in unprecedented detail.
MRI is a vital diagnostic and monitoring technique for chronic illnesses because it offers non-invasive, comprehensive insights into the anatomical and functional elements of the body. Furthermore, MRI's adaptability makes multi-parametric imaging possible, which promotes a comprehensive comprehension of the course of a disease. The demand for cutting-edge diagnostic instruments like MRI scanners is anticipated to increase due to the growing burden that chronic diseases are placing on healthcare systems around the globe. These tools are critical in addressing the healthcare issues brought on by the rising prevalence of chronic illnesses.
RestraintCompetition from alternative imaging modalities can hinder the magnetic resonance imaging scanners market during the forecast period.
The Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) scanners market will face significant competition from alternative imaging modalities during the forecast period. While MRI scanners have unrivaled advantages in terms of non-invasiveness, excellent soft tissue contrast, and the absence of ionizing radiation, alternative modalities such as X-rays and computed tomography (CT) scans remain viable options, especially in certain clinical scenarios. X-rays and CT scans are frequently regarded as more cost-effective and time-saving for routine checkups and emergency scenarios. Given the speed with which these modalities acquire and process images, they are preferable in urgent situations requiring speedy decision-making.
Furthermore, technological developments have increased the spatial resolution of CT scans, allowing for comprehensive imaging of anatomical features. Furthermore, emerging imaging technologies such as molecular imaging, positron emission tomography (PET), and hybrid imaging modalities are challenging MRI's supremacy in certain applications including oncology and cardiac imaging. The competitive landscape forces MRI makers to develop constantly, addressing issues about cost, accessibility, and speed in order to remain competitive in the face of alternative imaging modality. Despite MRI's distinct benefits, market operators must handle these hurdles strategically, stressing the technology's capabilities while adapting to changing healthcare demands in order to preserve and extend their market share.
OpportunitiesIntegration of artificial intelligence (AI) is projected to boost the demand for magnetic resonance imaging scanners market.
The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) is expected to be a game changer in increasing demand for Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) scanners in the healthcare market. AI applications in MRI scanners include a wide variety of operations, including image capture, reconstruction, and interpretation, resulting in increased efficiency, accuracy, and diagnostic capabilities. Machine learning algorithms can improve image processing by shortening acquisition times and refining scan parameters based on individual patient traits. Furthermore, AI-driven image reconstruction approaches help to improve image quality, reduce artifacts, and increase the diagnostic utility of MRI images.
AI's ability to automate and streamline the interpretation process is one of its major contributions to the MRI scanner market. AI systems can speed up the diagnostic process and increase overall accuracy by helping radiologists identify anomalies, segment anatomical structures, and even forecast disease outcomes. This may help with issues relating to the growing amount of data from medical imaging tests and the requirement for accurate and rapid diagnosis.
AI also makes it easier to build sophisticated imaging methods like quantitative imaging and functional MRI (fMRI), which allow for a more thorough evaluation of physiological processes and tissue properties. MRI scanners may now be used for more precise diagnosis thanks to artificial intelligence (AI), which also makes these machines essential for treatment planning and tailored therapy.
Magnetic Resonance Imaging Scanners Market Trends
-
The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning in MRI scanners has been a prominent trend. AI is being used for image processing, interpretation, and even predicting patient outcomes, thereby enhancing diagnostic accuracy and efficiency.
-
The market has seen a preference for high-field MRI systems (1.5T to 3T), driven by their superior image quality. Continued advancements in high-field technology have contributed to clearer and more detailed images.
-
There has been a growing focus on functional MRI, especially in neuroscience and neurology applications. fMRI allows for the mapping of brain activity, providing valuable insights into cognitive functions and neurological disorders.
-
Advancements in portable and point-of-care MRI technologies have gained attention. These innovations aim to increase accessibility to MRI in various settings, including remote areas and emergency situations.
-
The expanding applications of MRI in oncology, including tumor detection, characterization, and treatment response assessment, have been a notable trend. MRI's ability to provide detailed soft tissue imaging is particularly beneficial in oncological diagnostics.
-
The integration of MRI with other imaging modalities, such as positron emission tomography (PET-MRI) and single-photon emission computed tomography (SPECT-MRI), has been an emerging trend.
Competitive Landscape
The competitive landscape of the magnetic resonance imaging scanners market was dynamic, with several prominent companies competing to provide innovative and advanced magnetic resonance imaging scanners solutions.
- Siemens Healthineers
- GE Healthcare
- Philips Healthcare
- Toshiba Medical Systems Corporation
- Hitachi Medical Corporation
- Bruker Corporation
- Esaote SpA
- Fonar Corporation
- Mindray Medical International Limited
- Neusoft Medical Systems Co., Ltd.
- Samsung Medison Co., Ltd.
- Shenzhen Anke High-tech Co., Ltd.
- Time Medical Systems Co., Ltd.
- AllTech Medical Systems America, Inc.
- Aspect Imaging Ltd.
- Aurigin Technology Inc.
- CMR Naviscan Corporation
- Cubresa Inc.
- Mediso Ltd.
- MR Solutions Ltd.
-
January 17, 2024: Siemens Healthineers and City Cancer Challenge (C/Can) are expanding the geographical and technological scope of their partnership for the long term, building on their existing collaboration to enable more timely cancer diagnosis and treatment, and increase survivorship for patients in low- and middle-income countries.
-
February 8, 2024 – GE HealthCare (Nasdaq: GEHC), a leading global medical technology, pharmaceutical diagnostics, and digital solutions innovator, and MedQuest Associates (MedQuest), a leading owner, operator, and manager of outpatient diagnostic imaging facilities, announced a three-year collaboration to deliver excellence in patient care by providing access to innovative technologies from GE HealthCare and the infrastructure and resources from MedQuest that are needed to optimize multi-site outpatient imaging networks for success.
Regional Analysis
Asia-Pacific accounted for the largest market in the magnetic resonance imaging scanners market. Asia-Pacific accounted for 40 % market share of the global market value. the region's robust economic growth has led to increased healthcare expenditure, resulting in greater investments in advanced medical technologies, including MRI scanners. Moreover, the rising prevalence of chronic diseases and a growing aging population in countries such as China, Japan, and India have driven the demand for diagnostic imaging procedures, fostering the adoption of MRI scanners.
Furthermore, technological advancements and a focus on research and development in the healthcare sector have propelled the Asia-Pacific MRI scanners market forward. The region has witnessed collaborations between international medical equipment manufacturers and local healthcare institutions, facilitating the introduction of state-of-the-art MRI technologies. The increased awareness and understanding of the benefits of early disease detection and accurate diagnosis have also played a crucial role in boosting the demand for MRI scanners in the region.
[caption id="attachment_38440" align="aligncenter" width="665"]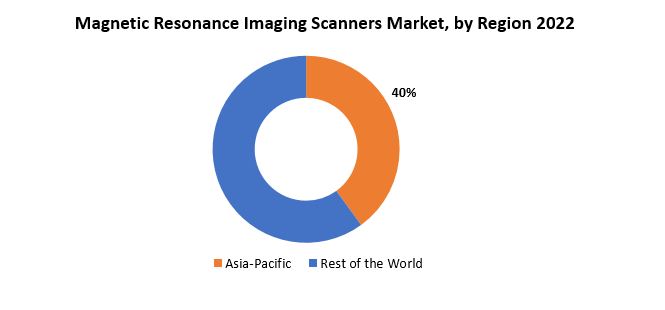
Government initiatives to enhance healthcare infrastructure and provide accessible and affordable healthcare services have been pivotal in the growth of the MRI scanners market in Asia-Pacific. Additionally, a surge in private investments in healthcare facilities, coupled with favorable reimbursement policies, has created a conducive environment for the expansion of the MRI scanners market in the region.
In Europe, countries like Germany, the United Kingdom, and France have witnessed significant growth in the MRI scanners market, driven by increasing incidences of chronic diseases, a rapidly aging population, and a strong emphasis on early and accurate diagnosis. The European market benefits from a collaborative approach between healthcare providers and medical device manufacturers, fostering innovation and the adoption of cutting-edge MRI technologies.
In North America, particularly in the United States and Canada, the MRI scanners market is well-established and highly competitive. The region boasts advanced healthcare facilities, a robust regulatory framework, and a high level of awareness among both healthcare professionals and the general population regarding the benefits of MRI diagnostics. The constant evolution of healthcare policies and reimbursement systems has further stimulated the demand for MRI scanners in these markets. The presence of key players and continuous investments in research and development contribute to the ongoing growth and sophistication of the MRI scanners market in North America.
Target Audience for Magnetic Resonance Imaging Scanners Market
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging Scanners Enthusiasts
- High-End Interior Designers
- Luxury Homeowners
- Upscale Restaurants and Hotels
- Collectors of Fine Tableware
- Event Planners for Exclusive Events
- Luxury Gift Buyers
- Affluent Consumers with Discerning Taste
- Luxury Retailers and Boutiques
- Interior Decorators for Luxury Properties
Segments Covered in the Magnetic Resonance Imaging Scanners Market Report
Magnetic Resonance Imaging Scanners Market by Field Strength- Low-to-mid-field MRI systems (0.5T to 1.5T)
- High-field MRI systems (1.5T to 3T)
- Very-high-field MRI systems (3T to 7T)
- Ultra-high-field MRI systems (7T and above)
- Neurology
- Musculoskeletal
- Oncology
- Cardiovascular
- Other Applications
- Hospitals
- Diagnostic Imaging Centers
- Other End Users
- North America
- Europe
- Asia Pacific
- South America
- Middle East and Africa
Key Question Answered
- What is the expected growth rate of the Magnetic Resonance Imaging Scanners market over the next 7 years?
- Who are the major players in the Magnetic Resonance Imaging Scanners market and what is their market share?
- What are the end-user industries driving market demand and what is their outlook?
- What are the opportunities for growth in emerging markets such as Asia-Pacific, the middle east, and Africa?
- How is the economic environment affecting the Magnetic Resonance Imaging Scanners market, including factors such as interest rates, inflation, and exchange rates?
- What is the expected impact of government policies and regulations on the Magnetic Resonance Imaging Scanners market?
- What is the current and forecasted size and growth rate of the global Magnetic Resonance Imaging Scanners market?
- What are the key drivers of growth in the Magnetic Resonance Imaging Scanners market?
- Who are the major players in the market and what is their market share?
- What are the distribution channels and supply chain dynamics in the Magnetic Resonance Imaging Scanners market?
- What are the technological advancements and innovations in the Magnetic Resonance Imaging Scanners market and their impact on product development and growth?
- What are the regulatory considerations and their impact on the market?
- What are the challenges faced by players in the magnetic resonance imaging scanners market and how are they addressing these challenges?
- What are the opportunities for growth and expansion in the Magnetic Resonance Imaging Scanners market?
- What are the product offerings and specifications of leading players in the market?
- INTRODUCTION
- MARKET DEFINITION
- MARKET SEGMENTATION
- RESEARCH TIMELINES
- ASSUMPTIONS AND LIMITATIONS
- RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
- DATA MINING
- SECONDARY RESEARCH
- PRIMARY RESEARCH
- SUBJECT-MATTER EXPERTS’ ADVICE
- QUALITY CHECKS
- FINAL REVIEW
- DATA TRIANGULATION
- BOTTOM-UP APPROACH
- TOP-DOWN APPROACH
- RESEARCH FLOW
- DATA SOURCES
- DATA MINING
- EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
- MARKET OVERVIEW
- MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET OUTLOOK
- MARKET DRIVERS
- MARKET RESTRAINTS
- MARKET OPPORTUNITIES
- IMPACT OF COVID-19 ON MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET
- PORTER’S FIVE FORCES MODEL
- THREAT FROM NEW ENTRANTS
- THREAT FROM SUBSTITUTES
- BARGAINING POWER OF SUPPLIERS
- BARGAINING POWER OF CUSTOMERS
- DEGREE OF COMPETITION
- INDUSTRY VALUE CHAIN ANALYSIS
- MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET OUTLOOK
- GLOBAL MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY FIELD STRENGTH, 2020-2030, (USD BILLION) (THOUSAND UNITS)
- LOW-TO-MID-FIELD MRI SYSTEMS (0.5T TO 1.5T)
- HIGH-FIELD MRI SYSTEMS (1.5T TO 3T)
- VERY-HIGH-FIELD MRI SYSTEMS (3T TO 7T)
- ULTRA-HIGH-FIELD MRI SYSTEMS (7T AND ABOVE)
- GLOBAL MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY APPLICATION, 2020-2030, (USD BILLION) (THOUSAND UNITS)
- NEUROLOGY
- MUSCULOSKELETAL
- ONCOLOGY
- CARDIOVASCULAR
- OTHER APPLICATIONS
- GLOBAL MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY END USER, 2020-2030, (USD BILLION) (THOUSAND UNITS)
- HOSPITALS
- DIAGNOSTIC IMAGING CENTERS
- OTHER END USERS
- GLOBAL MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY REGION, 2020-2030, (USD BILLION) (THOUSAND UNITS)
- NORTH AMERICA
- US
- CANADA
- MEXICO
- SOUTH AMERICA
- BRAZIL
- ARGENTINA
- COLOMBIA
- REST OF SOUTH AMERICA
- EUROPE
- GERMANY
- UK
- FRANCE
- ITALY
- SPAIN
- RUSSIA
- REST OF EUROPE
- ASIA PACIFIC
- INDIA
- CHINA
- JAPAN
- SOUTH KOREA
- AUSTRALIA
- SOUTH-EAST ASIA
- REST OF ASIA PACIFIC
- MIDDLE EAST AND AFRICA
- UAE
- SAUDI ARABIA
- SOUTH AFRICA
- REST OF MIDDLE EAST AND AFRICA
- NORTH AMERICA
- COMPANY PROFILES*
(BUSINESS OVERVIEW, COMPANY SNAPSHOT, PRODUCTS OFFERED, RECENT DEVELOPMENTS)
- SIEMENS HEALTHINEERS
- GE HEALTHCARE
- PHILIPS HEALTHCARE
- TOSHIBA MEDICAL SYSTEMS CORPORATION
- HITACHI MEDICAL CORPORATION
- BRUKER CORPORATION
- ESAOTE SPA
- FONAR CORPORATION
- MINDRAY MEDICAL INTERNATIONAL LIMITED
- NEUSOFT MEDICAL SYSTEMS CO., LTD.
- SAMSUNG MEDISON CO., LTD.
- SHENZHEN ANKE HIGH-TECH CO., LTD.
- TIME MEDICAL SYSTEMS CO., LTD.
- ALLTECH MEDICAL SYSTEMS AMERICA, INC.
- ASPECT IMAGING LTD.
- AURIGIN TECHNOLOGY INC.
- CMR NAVISCAN CORPORATION
- CUBRESA INC.
- MEDISO LTD.
- MR SOLUTIONS LTD.
*THE COMPANY LIST IS INDICATIVE
LIST OF TABLES
TABLE 1 GLOBAL MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY FIELD STRENGTH (USD BILLION) 2020-2030
TABLE 2 GLOBAL MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY FIELD STRENGTH (THOUSAND UNITS) 2020-2030
TABLE 3 GLOBAL MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY END USER (USD BILLION) 2020-2030
TABLE 4 GLOBAL MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY END USER (THOUSAND UNITS) 2020-2030
TABLE 5 GLOBAL MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY APPLICATION (USD BILLION) 2020-2030
TABLE 6 GLOBAL MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY APPLICATION (THOUSAND UNITS) 2020-2030
TABLE 7 GLOBAL MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY REGION (USD BILLION) 2020-2030
TABLE 8 GLOBAL MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY REGION (THOUSAND UNITS) 2020-2030
TABLE 9 NORTH AMERICA MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY COUNTRY (USD BILLION) 2020-2030
TABLE 10 NORTH AMERICA MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY COUNTRY (THOUSAND UNITS) 2020-2030
TABLE 11 NORTH AMERICA MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY FIELD STRENGTH (USD BILLION) 2020-2030
TABLE 12 NORTH AMERICA MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY FIELD STRENGTH (THOUSAND UNITS) 2020-2030
TABLE 13 NORTH AMERICA MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY END USER (USD BILLION) 2020-2030
TABLE 14 NORTH AMERICA MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY END USER (THOUSAND UNITS) 2020-2030
TABLE 15 NORTH AMERICA MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY APPLICATION (USD BILLION) 2020-2030
TABLE 16 NORTH AMERICA MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY APPLICATION (THOUSAND UNITS) 2020-2030
TABLE 17 US MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY FIELD STRENGTH (USD BILLION) 2020-2030
TABLE 18 US MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY FIELD STRENGTH (THOUSAND UNITS) 2020-2030
TABLE 19 US MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY END USER (USD BILLION) 2020-2030
TABLE 20 US MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY END USER (THOUSAND UNITS) 2020-2030
TABLE 21 US MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY APPLICATION (USD BILLION) 2020-2030
TABLE 22 US MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY APPLICATION (THOUSAND UNITS) 2020-2030
TABLE 23 CANADA MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY FIELD STRENGTH (USD BILLION) 2020-2030
TABLE 24 CANADA MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY FIELD STRENGTH (THOUSAND UNITS) 2020-2030
TABLE 25 CANADA MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY END USER (USD BILLION) 2020-2030
TABLE 26 CANADA MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY END USER (THOUSAND UNITS) 2020-2030
TABLE 27 CANADA MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY APPLICATION (USD BILLION) 2020-2030
TABLE 28 CANADA MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY APPLICATION (THOUSAND UNITS) 2020-2030
TABLE 29 MEXICO MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY FIELD STRENGTH (USD BILLION) 2020-2030
TABLE 30 MEXICO MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY FIELD STRENGTH (THOUSAND UNITS) 2020-2030
TABLE 31 MEXICO MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY END USER (USD BILLION) 2020-2030
TABLE 32 MEXICO MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY END USER (THOUSAND UNITS) 2020-2030
TABLE 33 MEXICO MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY APPLICATION (USD BILLION) 2020-2030
TABLE 34 MEXICO MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY APPLICATION (THOUSAND UNITS) 2020-2030
TABLE 35 SOUTH AMERICA MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY COUNTRY (USD BILLION) 2020-2030
TABLE 36 SOUTH AMERICA MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY COUNTRY (THOUSAND UNITS) 2020-2030
TABLE 37 SOUTH AMERICA MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY FIELD STRENGTH (USD BILLION) 2020-2030
TABLE 38 SOUTH AMERICA MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY FIELD STRENGTH (THOUSAND UNITS) 2020-2030
TABLE 39 SOUTH AMERICA MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY END USER (USD BILLION) 2020-2030
TABLE 40 SOUTH AMERICA MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY END USER (THOUSAND UNITS) 2020-2030
TABLE 41 SOUTH AMERICA MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY APPLICATION (USD BILLION) 2020-2030
TABLE 42 SOUTH AMERICA MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY APPLICATION (THOUSAND UNITS) 2020-2030
TABLE 43 BRAZIL MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY FIELD STRENGTH (USD BILLION) 2020-2030
TABLE 44 BRAZIL MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY FIELD STRENGTH (THOUSAND UNITS) 2020-2030
TABLE 45 BRAZIL MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY END USER (USD BILLION) 2020-2030
TABLE 46 BRAZIL MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY END USER (THOUSAND UNITS) 2020-2030
TABLE 47 BRAZIL MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY APPLICATION (USD BILLION) 2020-2030
TABLE 48 BRAZIL MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY APPLICATION (THOUSAND UNITS) 2020-2030
TABLE 49 ARGENTINA MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY FIELD STRENGTH (USD BILLION) 2020-2030
TABLE 50 ARGENTINA MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY FIELD STRENGTH (THOUSAND UNITS) 2020-2030
TABLE 51 ARGENTINA MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY END USER (USD BILLION) 2020-2030
TABLE 52 ARGENTINA MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY END USER (THOUSAND UNITS) 2020-2030
TABLE 53 ARGENTINA MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY APPLICATION (USD BILLION) 2020-2030
TABLE 54 ARGENTINA MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY APPLICATION (THOUSAND UNITS) 2020-2030
TABLE 55 COLOMBIA MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY FIELD STRENGTH (USD BILLION) 2020-2030
TABLE 56 COLOMBIA MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY FIELD STRENGTH (THOUSAND UNITS) 2020-2030
TABLE 57 COLOMBIA MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY END USER (USD BILLION) 2020-2030
TABLE 58 COLOMBIA MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY END USER (THOUSAND UNITS) 2020-2030
TABLE 59 COLOMBIA MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY APPLICATION (USD BILLION) 2020-2030
TABLE 60 COLOMBIA MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY APPLICATION (THOUSAND UNITS) 2020-2030
TABLE 61 REST OF SOUTH AMERICA MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY FIELD STRENGTH (USD BILLION) 2020-2030
TABLE 62 REST OF SOUTH AMERICA MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY FIELD STRENGTH (THOUSAND UNITS) 2020-2030
TABLE 63 REST OF SOUTH AMERICA MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY END USER (USD BILLION) 2020-2030
TABLE 64 REST OF SOUTH AMERICA MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY END USER (THOUSAND UNITS) 2020-2030
TABLE 65 REST OF SOUTH AMERICA MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY APPLICATION (USD BILLION) 2020-2030
TABLE 66 REST OF SOUTH AMERICA MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY APPLICATION (THOUSAND UNITS) 2020-2030
TABLE 67 ASIA-PACIFIC MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY COUNTRY (USD BILLION) 2020-2030
TABLE 68 ASIA-PACIFIC MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY COUNTRY (THOUSAND UNITS) 2020-2030
TABLE 69 ASIA-PACIFIC MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY FIELD STRENGTH (USD BILLION) 2020-2030
TABLE 70 ASIA-PACIFIC MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY FIELD STRENGTH (THOUSAND UNITS) 2020-2030
TABLE 71 ASIA-PACIFIC MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY END USER (USD BILLION) 2020-2030
TABLE 72 ASIA-PACIFIC MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY END USER (THOUSAND UNITS) 2020-2030
TABLE 73 ASIA-PACIFIC MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY APPLICATION (USD BILLION) 2020-2030
TABLE 74 ASIA-PACIFIC MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY APPLICATION (THOUSAND UNITS) 2020-2030
TABLE 75 INDIA MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY FIELD STRENGTH (USD BILLION) 2020-2030
TABLE 76 INDIA MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY FIELD STRENGTH (THOUSAND UNITS) 2020-2030
TABLE 77 INDIA MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY END USER (USD BILLION) 2020-2030
TABLE 78 INDIA MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY END USER (THOUSAND UNITS) 2020-2030
TABLE 79 INDIA MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY APPLICATION (USD BILLION) 2020-2030
TABLE 80 INDIA MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY APPLICATION (THOUSAND UNITS) 2020-2030
TABLE 81 CHINA MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY FIELD STRENGTH (USD BILLION) 2020-2030
TABLE 82 CHINA MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY FIELD STRENGTH (THOUSAND UNITS) 2020-2030
TABLE 83 CHINA MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY END USER (USD BILLION) 2020-2030
TABLE 84 CHINA MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY END USER (THOUSAND UNITS) 2020-2030
TABLE 85 CHINA MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY APPLICATION (USD BILLION) 2020-2030
TABLE 86 CHINA MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY APPLICATION (THOUSAND UNITS) 2020-2030
TABLE 87 JAPAN MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY FIELD STRENGTH (USD BILLION) 2020-2030
TABLE 88 JAPAN MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY FIELD STRENGTH (THOUSAND UNITS) 2020-2030
TABLE 89 JAPAN MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY END USER (USD BILLION) 2020-2030
TABLE 90 JAPAN MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY END USER (THOUSAND UNITS) 2020-2030
TABLE 91 JAPAN MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY APPLICATION (USD BILLION) 2020-2030
TABLE 92 JAPAN MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY APPLICATION (THOUSAND UNITS) 2020-2030
TABLE 93 SOUTH KOREA MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY FIELD STRENGTH (USD BILLION) 2020-2030
TABLE 94 SOUTH KOREA MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY FIELD STRENGTH (THOUSAND UNITS) 2020-2030
TABLE 95 SOUTH KOREA MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY END USER (USD BILLION) 2020-2030
TABLE 96 SOUTH KOREA MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY END USER (THOUSAND UNITS) 2020-2030
TABLE 97 SOUTH KOREA MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY APPLICATION (USD BILLION) 2020-2030
TABLE 98 SOUTH KOREA MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY APPLICATION (THOUSAND UNITS) 2020-2030
TABLE 99 AUSTRALIA MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY FIELD STRENGTH (USD BILLION) 2020-2030
TABLE 100 AUSTRALIA MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY FIELD STRENGTH (THOUSAND UNITS) 2020-2030
TABLE 101 AUSTRALIA MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY END USER (USD BILLION) 2020-2030
TABLE 102 AUSTRALIA MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY END USER (THOUSAND UNITS) 2020-2030
TABLE 103 AUSTRALIA MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY APPLICATION (USD BILLION) 2020-2030
TABLE 104 AUSTRALIA MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY APPLICATION (THOUSAND UNITS) 2020-2030
TABLE 105 SOUTH-EAST ASIA MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY FIELD STRENGTH (USD BILLION) 2020-2030
TABLE 106 SOUTH-EAST ASIA MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY FIELD STRENGTH (THOUSAND UNITS) 2020-2030
TABLE 107 SOUTH-EAST ASIA MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY END USER (USD BILLION) 2020-2030
TABLE 108 SOUTH-EAST ASIA MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY END USER (THOUSAND UNITS) 2020-2030
TABLE 109 SOUTH-EAST ASIA MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY APPLICATION (USD BILLION) 2020-2030
TABLE 110 SOUTH-EAST ASIA MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY APPLICATION (THOUSAND UNITS) 2020-2030
TABLE 111 REST OF ASIA PACIFIC MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY FIELD STRENGTH (USD BILLION) 2020-2030
TABLE 112 REST OF ASIA PACIFIC MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY FIELD STRENGTH (THOUSAND UNITS) 2020-2030
TABLE 113 REST OF ASIA PACIFIC MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY END USER (USD BILLION) 2020-2030
TABLE 114 REST OF ASIA PACIFIC MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY END USER (THOUSAND UNITS) 2020-2030
TABLE 115 REST OF ASIA PACIFIC MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY APPLICATION (USD BILLION) 2020-2030
TABLE 116 REST OF ASIA PACIFIC MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY APPLICATION (THOUSAND UNITS) 2020-2030
TABLE 117 EUROPE MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY COUNTRY (USD BILLION) 2020-2030
TABLE 118 EUROPE MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY COUNTRY (THOUSAND UNITS) 2020-2030
TABLE 119 EUROPE MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY FIELD STRENGTH (USD BILLION) 2020-2030
TABLE 120 EUROPE MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY FIELD STRENGTH (THOUSAND UNITS) 2020-2030
TABLE 121 EUROPE MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY END USER (USD BILLION) 2020-2030
TABLE 122 EUROPE MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY END USER (THOUSAND UNITS) 2020-2030
TABLE 123 EUROPE MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY APPLICATION (USD BILLION) 2020-2030
TABLE 124 EUROPE MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY APPLICATION (THOUSAND UNITS) 2020-2030
TABLE 125 GERMANY MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY FIELD STRENGTH (USD BILLION) 2020-2030
TABLE 126 GERMANY MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY FIELD STRENGTH (THOUSAND UNITS) 2020-2030
TABLE 127 GERMANY MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY END USER (USD BILLION) 2020-2030
TABLE 128 GERMANY MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY END USER (THOUSAND UNITS) 2020-2030
TABLE 129 GERMANY MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY APPLICATION (USD BILLION) 2020-2030
TABLE 130 GERMANY MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY APPLICATION (THOUSAND UNITS) 2020-2030
TABLE 131 UK MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY FIELD STRENGTH (USD BILLION) 2020-2030
TABLE 132 UK MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY FIELD STRENGTH (THOUSAND UNITS) 2020-2030
TABLE 133 UK MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY END USER (USD BILLION) 2020-2030
TABLE 134 UK MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY END USER (THOUSAND UNITS) 2020-2030
TABLE 135 UK MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY APPLICATION (USD BILLION) 2020-2030
TABLE 136 UK MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY APPLICATION (THOUSAND UNITS) 2020-2030
TABLE 137 FRANCE MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY FIELD STRENGTH (USD BILLION) 2020-2030
TABLE 138 FRANCE MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY FIELD STRENGTH (THOUSAND UNITS) 2020-2030
TABLE 139 FRANCE MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY END USER (USD BILLION) 2020-2030
TABLE 140 FRANCE MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY END USER (THOUSAND UNITS) 2020-2030
TABLE 141 FRANCE MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY APPLICATION (USD BILLION) 2020-2030
TABLE 142 FRANCE MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY APPLICATION (THOUSAND UNITS) 2020-2030
TABLE 143 ITALY MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY FIELD STRENGTH (USD BILLION) 2020-2030
TABLE 144 ITALY MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY FIELD STRENGTH (THOUSAND UNITS) 2020-2030
TABLE 145 ITALY MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY END USER (USD BILLION) 2020-2030
TABLE 146 ITALY MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY END USER (THOUSAND UNITS) 2020-2030
TABLE 147 ITALY MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY APPLICATION (USD BILLION) 2020-2030
TABLE 148 ITALY MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY APPLICATION (THOUSAND UNITS) 2020-2030
TABLE 149 SPAIN MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY FIELD STRENGTH (USD BILLION) 2020-2030
TABLE 150 SPAIN MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY FIELD STRENGTH (THOUSAND UNITS) 2020-2030
TABLE 151 SPAIN MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY END USER (USD BILLION) 2020-2030
TABLE 152 SPAIN MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY END USER (THOUSAND UNITS) 2020-2030
TABLE 153 SPAIN MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY APPLICATION (USD BILLION) 2020-2030
TABLE 154 SPAIN MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY APPLICATION (THOUSAND UNITS) 2020-2030
TABLE 155 RUSSIA MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY FIELD STRENGTH (USD BILLION) 2020-2030
TABLE 156 RUSSIA MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY FIELD STRENGTH (THOUSAND UNITS) 2020-2030
TABLE 157 RUSSIA MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY END USER (USD BILLION) 2020-2030
TABLE 158 RUSSIA MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY END USER (THOUSAND UNITS) 2020-2030
TABLE 159 RUSSIA MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY APPLICATION (USD BILLION) 2020-2030
TABLE 160 RUSSIA MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY APPLICATION (THOUSAND UNITS) 2020-2030
TABLE 161 REST OF EUROPE MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY FIELD STRENGTH (USD BILLION) 2020-2030
TABLE 162 REST OF EUROPE MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY FIELD STRENGTH (THOUSAND UNITS) 2020-2030
TABLE 163 REST OF EUROPE MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY END USER (USD BILLION) 2020-2030
TABLE 164 REST OF EUROPE MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY END USER (THOUSAND UNITS) 2020-2030
TABLE 165 REST OF EUROPE MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY APPLICATION (USD BILLION) 2020-2030
TABLE 166 REST OF EUROPE MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY APPLICATION (THOUSAND UNITS) 2020-2030
TABLE 167 MIDDLE EAST AND AFRICA MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY COUNTRY (USD BILLION) 2020-2030
TABLE 168 MIDDLE EAST AND AFRICA MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY COUNTRY (THOUSAND UNITS) 2020-2030
TABLE 169 MIDDLE EAST AND AFRICA MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY FIELD STRENGTH (USD BILLION) 2020-2030
TABLE 170 MIDDLE EAST AND AFRICA MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY FIELD STRENGTH (THOUSAND UNITS) 2020-2030
TABLE 171 MIDDLE EAST AND AFRICA MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY END USER (USD BILLION) 2020-2030
TABLE 172 MIDDLE EAST AND AFRICA MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY END USER (THOUSAND UNITS) 2020-2030
TABLE 173 MIDDLE EAST AND AFRICA MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY APPLICATION (USD BILLION) 2020-2030
TABLE 174 MIDDLE EAST AND AFRICA MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY APPLICATION (THOUSAND UNITS) 2020-2030
TABLE 175 UAE MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY FIELD STRENGTH (USD BILLION) 2020-2030
TABLE 176 UAE MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY FIELD STRENGTH (THOUSAND UNITS) 2020-2030
TABLE 177 UAE MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY END USER (USD BILLION) 2020-2030
TABLE 178 UAE MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY END USER (THOUSAND UNITS) 2020-2030
TABLE 179 UAE MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY APPLICATION (USD BILLION) 2020-2030
TABLE 180 UAE MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY APPLICATION (THOUSAND UNITS) 2020-2030
TABLE 181 SAUDI ARABIA MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY FIELD STRENGTH (USD BILLION) 2020-2030
TABLE 182 SAUDI ARABIA MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY FIELD STRENGTH (THOUSAND UNITS) 2020-2030
TABLE 183 SAUDI ARABIA MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY END USER (USD BILLION) 2020-2030
TABLE 184 SAUDI ARABIA MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY END USER (THOUSAND UNITS) 2020-2030
TABLE 185 SAUDI ARABIA MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY APPLICATION (USD BILLION) 2020-2030
TABLE 186 SAUDI ARABIA MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY APPLICATION (THOUSAND UNITS) 2020-2030
TABLE 187 SOUTH AFRICA MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY FIELD STRENGTH (USD BILLION) 2020-2030
TABLE 188 SOUTH AFRICA MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY FIELD STRENGTH (THOUSAND UNITS) 2020-2030
TABLE 189 SOUTH AFRICA MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY END USER (USD BILLION) 2020-2030
TABLE 190 SOUTH AFRICA MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY END USER (THOUSAND UNITS) 2020-2030
TABLE 191 SOUTH AFRICA MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY APPLICATION (USD BILLION) 2020-2030
TABLE 192 SOUTH AFRICA MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY APPLICATION (THOUSAND UNITS) 2020-2030
TABLE 193 REST OF MIDDLE EAST AND AFRICA MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY FIELD STRENGTH (USD BILLION) 2020-2030
TABLE 194 REST OF MIDDLE EAST AND AFRICA MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY FIELD STRENGTH (THOUSAND UNITS) 2020-2030
TABLE 195 REST OF MIDDLE EAST AND AFRICA MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY END USER (USD BILLION) 2020-2030
TABLE 196 REST OF MIDDLE EAST AND AFRICA MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY END USER (THOUSAND UNITS) 2020-2030
TABLE 197 REST OF MIDDLE EAST AND AFRICA MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY APPLICATION (USD BILLION) 2020-2030
TABLE 198 REST OF MIDDLE EAST AND AFRICA MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY APPLICATION (THOUSAND UNITS) 2020-2030
LIST OF FIGURES
FIGURE 1 MARKET DYNAMICS
FIGURE 2 MARKET SEGMENTATION
FIGURE 3 REPORT TIMELINES: YEARS CONSIDERED
FIGURE 4 DATA TRIANGULATION
FIGURE 5 BOTTOM-UP APPROACH
FIGURE 6 TOP-DOWN APPROACH
FIGURE 7 RESEARCH FLOW
FIGURE 8 GLOBAL MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY FIELD STRENGTH (USD BILLION) 2020-2030
FIGURE 9 GLOBAL MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY APPLICATION (USD BILLION) 2020-2030
FIGURE 10 GLOBAL MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY END USER (USD BILLION) 2020-2030
FIGURE 11 GLOBAL MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY REGION (USD BILLION) 2020-2030
FIGURE 12 PORTER’S FIVE FORCES MODEL
FIGURE 13 GLOBAL MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY FIELD STRENGTH (USD BILLION) 2022
FIGURE 14 GLOBAL MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY APPLICATION (USD BILLION) 2022
FIGURE 15 GLOBAL MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY END USER (USD BILLION) 2022
FIGURE 16 GLOBAL MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANNERS MARKET BY REGION (USD BILLION) 2021
FIGURE 17 MARKET SHARE ANALYSIS
FIGURE 18 SIEMENS HEALTHINEERS: COMPANY SNAPSHOT
FIGURE 19 GE HEALTHCARE: COMPANY SNAPSHOT
FIGURE 20 PHILIPS HEALTHCARE: COMPANY SNAPSHOT
FIGURE 21 TOSHIBA MEDICAL SYSTEMS CORPORATION: COMPANY SNAPSHOT
FIGURE 22 HITACHI MEDICAL CORPORATION: COMPANY SNAPSHOT
FIGURE 23 BRUKER CORPORATION: COMPANY SNAPSHOT
FIGURE 24 ESAOTE SPA: COMPANY SNAPSHOT
FIGURE 25 FONAR CORPORATION: COMPANY SNAPSHOT
FIGURE 26 MINDRAY MEDICAL INTERNATIONAL LIMITED: COMPANY SNAPSHOT
FIGURE 27 NEUSOFT MEDICAL SYSTEMS CO., LTD.: COMPANY SNAPSHOT
FIGURE 28 SAMSUNG MEDISON CO., LTD.: COMPANY SNAPSHOT
FIGURE 29 SHENZHEN ANKE HIGH-TECH CO., LTD.: COMPANY SNAPSHOT
FIGURE 30 TIME MEDICAL SYSTEMS CO., LTD.: COMPANY SNAPSHOT
FIGURE 31 ALLTECH MEDICAL SYSTEMS AMERICA, INC.: COMPANY SNAPSHOT
FIGURE 32 ASPECT IMAGING LTD.: COMPANY SNAPSHOT
FIGURE 33 AURIGIN TECHNOLOGY INC.: COMPANY SNAPSHOT
FIGURE 34 CMR NAVISCAN CORPORATION: COMPANY SNAPSHOT
FIGURE 35 CUBRESA INC.: COMPANY SNAPSHOT
FIGURE 36 MEDISO LTD.: COMPANY SNAPSHOT
FIGURE 37 MR SOLUTIONS LTD.: COMPANY SNAPSHOT
DOWNLOAD FREE SAMPLE REPORT
License Type
SPEAK WITH OUR ANALYST
Want to know more about the report or any specific requirement?
WANT TO CUSTOMIZE THE REPORT?
Our Clients Speak
We asked them to research ‘ Equipment market’ all over the world, and their whole arrangement was helpful to us. thehealthanalytics.com insightful analysis and reports contributed to our current analysis and in creating a future strategy. Besides, the te
Yosuke Mitsui
Senior Associate Construction Equipment Sales & Marketing
We asked them to research ‘Equipment market’ all over the world, and their whole arrangement was helpful to us. thehealthanalytics.com insightful analysis and reports contributed to our current analysis and in creating a future strategy. Besides, the te






